What space will be required for the production workshop.
Laminate is made from wood that has been debarked and crushed. A high-density slab is created from the chips. The moisture resistance and strength of the finished product depends on the degree of density. The manufacturing process is quite complex, requiring the use of specific equipment, so the workshop must be spacious. Also, pay attention to the humidity in the room, since the laminate does not have special moisture-resistant qualities. The rented workshop must be heated, with a size of about 2,000 sq.m. Depending on the cost of rent in a certain city, the price can be $ 1-5 per 1 sq.m.
Staff for laminate business.
Directly for the production process, at least 15 people with experience in similar work will be needed. The salary of such an employee is from $ 500 per month. For the delivery of finished products, you need to hire drivers, possibly with your own car. The driver's salary will be from $ 400 and depreciation costs are possible. To service the ordering and delivery process, 2-3 operators and 4 loaders will be needed. These are not highly qualified personnel, their salary can be about $400. For operators, you can introduce a motivational program, with bonuses, depending on the volume of orders. This will make them interested in quality customer service. To account for doing business and filling out accounting reports, you need to hire an accountant with work experience, whose salary is calculated from $ 800.
Equipment selection.
|
|
Laminate production takes place in several stages:
1. Wood board manufacturing.
2. Saturation of the top layer with chemicals.
3. Facing.
4. Sawing panels according to the specified dimensions.
5. Packing.
In this regard, to create a business in the field of laminate production, you will need certain equipment: a cleaning machine, a machine, a drying chamber, a packaging machine. The minimum cost of all of the above is from $ 500,000. To ensure the acceptance of orders and record keeping, you will need computers, telephones and other equipment (the cost is from $ 10,000).
Search for clients. Use of effective advertising media.
For this production, the most effective will be the search for customers through Internet resources. To do this, you need to create your own website (cost from $100) and effectively "promote" it in the network (depending on the required traffic, the cost of the service is $200-800). The site must be filled with up-to-date information about the quality and cost of the laminate, indicate the methods of ordering, delivery, contact information, and create a feedback form. All this information takes part in the promotion of the site through search engines (SEO promotion). It is better to entrust the writing of texts to professionals who will write them according to the requests of potential customers and increase the possibility of bringing the site to the TOP. This will allow customers to find the company themselves. Additionally, you need to launch an advertising campaign that includes contextual and targeted advertising (cost from $200). You can order all these events in a specialized company that will provide a discount for a complex order.
Sales of finished products.
For this field of activity, the optimal distribution process would be delivery directly to the client, without the participation of intermediaries. It is better to arrange the process in such a way as to ensure delivery in the shortest possible time. The cost and conditions must be written on the site and announced to customers when ordering, in order to avoid misunderstandings. It will also serve as a competitive advantage for the company to provide free delivery from a certain order amount or to regular customers. In order to establish uninterrupted work, it is necessary to clearly understand the volume of deliveries, take into account the time of unloading / loading of goods, the time for delivery, and also correctly calculate the work schedule of drivers. The second option for the distribution line, which is better to establish when production volumes increase significantly, is the creation of a dealer network.
Required investment in the workshop.
Investments in the production of the business will amount to $524,000, excluding the cost of purchasing raw materials, the volume of which will be determined depending on the breadth of the market and the frequency of receiving orders.
- Equipment - from $510,000;
- Rent - from $2,000 per month;
- Payroll fund - from $11,000 per month;
- Marketing (website creation, advertising) - $800.
It is also necessary to take into account the costs of product certification. In the production of laminate, chemicals are used, so the availability of technical specifications for production and a hygiene certificate for products is mandatory. There are companies that carry out the necessary analysis of products and issue certified documentation.
Business payback.
The profitability of the laminate business is an average of 30%. The payback of the project is about 12-15 months. To reduce the payback period, it is necessary to properly establish the production process, follow the technology, produce high-quality goods, hire qualified workers, create a constant customer flow through advertising campaigns, set a competitive price and vary it according to market fluctuations, ensure uninterrupted supply.
Demand for laminate flooring will double in 2010. Growth in the laminate flooring market will be driven by the trend towards laminate flooring replacing primarily PVC (linoleum) flooring. At the same time, the main trend in the development of the laminate flooring market will be the displacement of imported products by Russian laminate.
All global manufacturers of laminate flooring carry out a full cycle of work, including:
- Production of fibreboard base
- Slab cladding
- Milling floor panels
Technology for the production of wood fiber boards (MDF)
Preparation of raw materials (wood chips production)
The roundwood is subjected to debarking (wood debarking) in a drum debarker. Then the logs cleared of bark enter the chipper, in which chips are obtained (chipping).
The wood chips pass through a screening system, where mechanical sorting is divided into large and small fractions. The sorted chips from the sorting plant are fed directly to the chip washing separator by means of a belt conveyor. All small foreign inclusions that may be in the wood chips (dirt, sand, small stones, glass, etc.) are washed out with hot water and settle at the bottom of the container.
After washing, the chips enter the bunker, where they are heated with steam up to 95-100 degrees Celsius, in order to ensure that - regardless of weather conditions - the same temperature and humidity of the chips at the entrance to the press.
Then the material falls for several minutes into another container, where, under high pressure of hot steam, we heat up to 165-175 degrees.
Heated chips become very plastic - it can be crushed with high quality without spending a lot of energy. The chips of the desired fraction, cleared of impurities, are ready for grinding into fiber.
Fiber preparation
Chips are crushed into fiber in a refiner (defibrator). This is the only comminution in the MDF production chain (unlike fibreboard, where the comminution is done mechanically in two stages).
At the outlet of the refiner, binders are added to the wood pulp, including resins, paraffin emulsion (resin & wax) and - if necessary - hardeners.
The resulting wood pulp enters the dryer. The structure of the dryer can be a conventional one-stage pneumatic type (pipe type) or a two-stage design.
The task of the dryer is not only to dry, but also to equalize the moisture content of the material by the volume of the wood pulp (the moisture content of the wood pulp at the outlet of the dryer should not exceed 8-9%).
After the dryer, air must be drawn out of the wood pulp, which is achieved with the help of cyclones.
An air separator can also be mounted on the conveyor, where a large fraction of the fiber is taken (quality control of grinding on the refiner - a large fraction can be obtained from insufficient or insufficiently uniform heating of the fiber before grinding on the refiner).
Carpet shaping and pressing
The carpet forming section consists of two parts - a storage hopper, where a supply of wood pulp is stored for work for 6-8 minutes, and a directly forming machine (mat former). The fiber is fed by a unit that evenly distributes it across the entire width of the dosing bin.
The forming machine is a series of roller guides that feed and align the fiber on the conveyor belt. Several take-off rollers evenly feed the fiber coming from the dosing hopper to the guide plate, which then enters the forming head. Forming rollers distribute the fiber in a given technological mode to the bottom forming conveyor. The forming rollers are adjusted in height and distribute the fiber evenly over the entire width of the forming carpet. The installation of leveling rollers, working on top of the formed carpet, ensures its even surface.
The formed carpet is weighed with high precision on a belt scale. Depending on the weighing results, the speed of the conveyor of the dosing hopper of the forming plant is adjusted.
The finished carpet goes to pre-pressing (prepressing), where the processes of squeezing air out of the volume of the slab take place - in a special area with a perforated tape. Effective pre-pressing ensures the integrity of the carpet before the press.
The thickness of the slab here decreases by 4-7 times, after which the carpet already becomes like a thick loose slab of a given width (equal to the width of the conveyor belt) - in this form it is fed to the main press (mat conveying).
Pressing
Three types of presses can be used: multi-deck, single-deck and continuous.
The continuous press is equally suitable for the production of MDF, chipboard and OSB boards. Its advantages:
- increase in productivity by 10-20%,
- reducing the thickness variation of finished products,
- quality improvement,
- simplified maintenance, minimum installation costs.
Multi-storey type presses have earned a good reputation for their high reliability. Its advantages:
- uniform heating of the entire heating plate,
- reliable hydraulic system,
- automatic control system,
- simultaneous mechanism,
- the possibility of producing door panels.
The single-deck press is designed to increase the return on investment for low capacity lines. The features of this type of press are:
- rapid change in production parameters,
- carrying out changes in the length and width of the plates,
- providing accurate board widths and fast pressing cycles.
Intermediate warehouse and finishing
The final processing of the board is one of the key processes in the production of MDF and includes: the line for unloading the press, intermediate storage, sanding line, cutting to size, packing line.
Unloading lines
After pressing, the excess width is cut off "on the go" with a special trimming saw. Then the "endless" MDF tape leaving the press is cut by a dividing saw moving relative to the observer at the speed of the board moving along the conveyor (sawing). Thus, also "on the go", rectangular slabs of the required format are obtained.
These plates enter the fan cooler (cooling), where they are cooled for 20-25 minutes. Fan coolers provide efficient and reliable cooling of plates prior to stacking. The number of fans is designed according to the capacity of the plant in order to ensure the optimal temperature of the slab before stacking.
Intermediate storage
It can be carried out "manually" (using loading machines) or be fully automated and provide real-time management of the warehouse using a computer control system.
Grinding line
Plates after the press may have a certain thickness difference, surface defects. These shortcomings are eliminated in the process of calibration and grinding, carried out in wide-belt multi-unit machines.
Cut slabs to size
Nowadays, it is becoming more and more necessary to have a cutting system that can quickly adapt to the needs of the customer. Cuttings from sawing after processing in a crusher or chipper are sent to a power plant.
Packing line
Packaging lines can be easily adapted to different package sizes and packaging materials.
Cladding of fibreboards
Two different processes are used for cladding fibreboards with paper-resin films: laminating (HPL - High Pressure Laminate technology) and laminating (DPL - Direct Pressure Laminate technology). There is also the ELESGO (elektronenstrahlgehaertete Oberflaeche) technology developed by HDM and DTS.
Board lamination (HPL technology - High Pressure Laminate)
Laminate production began with HPL (High Pressure Laminate) technology.
Laminating called the technology of facing wood-based panels, in which the film, continuously fed from a roll, is rolled onto a surface previously smeared with glue. You can roll the film on both plates simultaneously.
Conditionally distinguish between cold, warm and hot laminating.
Cold it is used when veneering with non-heat-resistant films, mainly synthetic ones, using PVA-adhesives. The curing of the adhesive usually takes place in a foot with a slight load from above.
At warm In laminating, glue is applied to a non-cooled (or preheated) surface, which helps to evaporate moisture from it and accelerate the curing process. In this case, the swelling of the plate occurs evenly and its structure will not appear on the outer side of the cladding. For the final setting of the adhesive, the products are kept in the foot. This method is suitable for facing boards with melamine films, including those with a finish effect.
The most common is hot laminating, which is also thermal laminating, in which various adhesives, including carbamide ones, are applicable. Glue and hardener are applied to the surface of the wood board, and the facing material is rolled onto it with heated rollers. Due to rather high temperatures and humidity, not only elastic, but also plastic deformations of the surface occur during thermal laminating. It is the latter that cause the effect of "smoothing", that is, the formation of a more stable lining than with cold laminating. After heat lamination, the boards can be immediately processed on circular saws.
For lamination, calender presses are used, their combinations with one-story positional short-cycle presses, as well as two-belt feed-through presses.
The domestic laminating line with a calender press, schematically shown in Figure 2.1, is designed for one- and two-sided facing with paper-resin films of chipboard or fiber boards with a thickness of 2.5 to 40 mm and a width of up to 1850 mm.
Drawing "Scheme of a laminating line based on a calender press"

1 - roller conveyor, 2 - lifting table, 3 - brush machine, 4 - roller machine for hardener application,
5 - channel for infrared drying of the hardener, 6 - gluing machine, 7 - roller conveyor,
8 - calender press (laminator), 9 - film cutter, 10 - belt conveyor, 11 - receiving table
The technological process begins with cleaning the plates from dust in a brush machine: its brushes with a diameter of 280 mm rotate at a speed of 300 rpm, the swept dust is removed through an exhauster.
On the intermediate roller conveyor, the base plate is fed into the roller machine, where a hardener solution is applied to one or both layers. For carbamide resins, an acid hardener is used at a concentration of 20–30%, with a pH value of not more than 2.5 and a viscosity of 20–70 s according to VZ-4. Consumption of hardener is approximately 30–35 g/m2.
After applying the hardener, the slab passes through an infrared dryer to remove the solvent and then is fed into a glue application machine, where a thermosetting resin is applied on a uniformly dried hardener at a concentration of up to 70%, with a viscosity of 100–140 s according to VZ-4 and an initial acidity of pH = 7–8 ,5. The gelatinization time of the resin applied over the hardener should be no more than 50 seconds at a temperature of 100 °C. Resin consumption 100–120 g/m2.
Next, the plate is passed through a roller press, in which a paper-resin film is rolled onto the prepared plate. The rollers are heated with thermal oil at a temperature of about 200 °C. The gap between the laminating rollers, adjustable from the control panel, must be 0.1 mm less than the thickness of the base plate. High-quality cladding is possible only with a sufficiently stable thickness of the plates in the batch - the spread should be within ± 0.2 mm. Lined boards after cutting off the film are delivered to the receiving table and stacked in a stack. The feed rate in such a line is 12–17 m/min.
When using films on which a layer of dried thermoplastic adhesive has already been applied or films with incompletely cured melamine-containing resin, the technological process is greatly simplified. There is no need to apply and dry a hardener and to apply a thermosetting resin to the face. The base plate immediately after cleaning goes to the roller laminating machine.
Figure 2.2 shows a general view of the installation for continuous thermal laminating of boards.
Drawing "Press of continuous action for laminating wood-based panels"

1 - steel belts, 2 - driven drums, 3 - tensioner, 4 - base, 5 - frame, 6 - drive drums
The press has two drive drums and two driven drums, on which steel bands are stretched.
The sliding of the belts over the hot plates is ensured by means of an air cushion, so the drum drive power is only 8–9 kW. The press operates at a constant working pressure (not more than 2 MPa), feed rate up to 16 m/min. Dust-free slabs are fed end-to-end one after the other to the area of double-sided cladding. The film from rolls, stretched from above and below on continuously moving plates, is cured in a belt press. At the exit from the press, a machine for milling longitudinal edges (removing overhangs) and a diagonal saw for transverse cutting of plates are provided.
Laminating is a cheaper and easier way to decorate polished slabs. However, laminated boards noticeably lose to laminated boards in a number of important indicators that affect the durability of products (wear resistance, resistance to high temperatures, etc.). In addition, when laminating, it is impossible to give the surface of the board a structural pattern (imitation of wood pores, orange peel, etc.) - laminated board can only be smooth. The only advantage of laminated boards today is their low cost, but this “advantage” quickly turns into a disadvantage and additional costs in the operation of furniture made from laminated boards.
Figure "Structure of HPL laminate"

1. Composite coating
2. Glue
3. Base plate
4. Glue
5. Stabilizing layer
Source: from the website "Association of European Producers of Laminate Flooring"
Plate lamination (DPL technology - Direct Pressure Laminate)
lamination in board production, it is called pressing sheets of the same format onto the surface of the board from impregnated papers with incompletely cured resin. These are usually melamine-containing resins that are cured by setting to the substrate in a hot press, so no adhesive is required on the surface of the board. That part of the resin, which is squeezed out on the surfaces facing the gasket sheets of the press, perceives the structure of the latter. By using appropriate spacers, it is possible to obtain lined boards with a smooth or embossed surface.
Depending on the purpose of the lined slab, its coating can be single or multilayer. Floor boards on top of the decorative film must have a strong protective layer - overlay. In order to avoid warping of the shield, a coating is also applied to its non-front face - the so-called compensating layer. After the final curing, the resin turns into a thermosetting polymer, and the resulting board is a composite material resembling laminated plastic in structure, but instead of kraft paper, a rigid substrate, that is, a base board, is used.
In the past, multi-storey hot presses borrowed from the plywood industry were the main laminating equipment. As the demand for high gloss furniture parts increased, these presses began to use polished steel pans and cool the press plates before relieving pressure. Polished pallets require very careful handling, even sanding dust and fingerprints on them can reduce the quality of the lining. Therefore, the lamination area must be kept impeccably clean, and the staff must work in special clothes and shoes.
The lining cycle in a multi-storey press lasts several minutes, during which time the press plates cool down so that some pallets can be unloaded and others loaded. Due to the need to remove the hot coolant, and then again bring it to the operating temperature, the energy consumption when using multi-storey presses is quite high.
Highly mechanized and automated lines based on such presses make it possible to realize a high curing rate of impregnating resins. The line, shown schematically in Figure 2.4, includes a device for piece-by-piece feeding of plates, a brush machine for cleaning them, devices for assembling packages and quickly loading them into a press.
Drawing "Scheme of the lamination line"

1 - supply of plates from a stack, 2 - supply of facing paper and formation of packages, 3 - loading of packages,
4 - hot short-cycle press, 5 - device for changing the gasket sheets of the press, 6 - longitudinal trimming of plates,
7 - transverse cutting and cleaning of slabs, 8 - sorting with stacking
To emboss the surface in order to obtain a non-smooth, porous structure, the press is equipped with special pallets, a device for quick pallet change is provided.
During the formation of the package, the sheets of facing material are very precisely fixed on the base plate in an electrostatic way. The assembled three-layer bag is automatically transferred to the press, which closes very quickly to keep open time to a minimum. Operating temperatures of the press are 180–200 °C. At such a high temperature, the resin in the composition of the facing material melts and cures, and after pressing it turns into a monolithic surface layer of the plate.
The pressure in the hot press is 3.5–4.5 MPa with the difference in thickness of the facing plates within ± 0.3 mm. If the spread in thickness does not exceed ±0.2 mm, the pressure can be reduced to 2.5–3.5 MPa.
The veneering pressing cycle consists of the following steps:
- pressure reduction in the press,
- quick opening of the press,
- unloading the lined slab with simultaneous loading of a new package,
- quick closing of the press,
- increase in pressure
- holding pressure.
Typically, standard equipment on such installations makes it possible to obtain a matte facing of the plate. To obtain glossy facings, polished steel sheets are used as pressing surfaces, and a high gloss in a laminated coating can only be achieved in multi-storey presses with cooling of the working plates.
At modern enterprises, the areas for facing slabs are almost completely automated and require a small number of maintenance personnel.
Laminated boards are more resistant to wear, high temperatures, etc. than laminated boards.
Figure "Structure of DPL laminate"

1. Protective layer (Overlay)
2. Decorative layer (paper)
3. Base plate
4. Stabilizing layer
Business in the production of laminate: how to open, succeed, and make a profit in this direction?
The most modern and convenient flooring material available in the segment is laminate, which is presented in the form of small sheets with spikes and grooves along the edges of the perimeter for connecting with each other. Due to the ease of installation, excellent technical characteristics and the average price range, it is becoming the most popular flooring.
The modern market of laminated coatings is represented by both domestic and foreign manufacturers. The competition between them is quite high, but despite this, there is still an opportunity to occupy free market segments by searching for some interesting and unexpected design solutions or their own pricing policy.
Profitability and financial aspects in the production of laminate.
According to preliminary estimates, the profitability of this kind of activity is quite high and reaches about 30-35%. A small plant is capable of producing up to 15 million square meters of laminate annually.
At the same time, the cost of the simplest production line will be about 20 million rubles. Now, to this amount, you need to add the cost of renting workshops and paying utility bills, obtaining permits and certification, salaries to staff, and the cost of raw materials. Do not forget to add another 30% to the resulting amount - these will be funds for unforeseen expenses. The amount is quite impressive, but this is not the main difficulty.
Difficulties faced by everyone who wants to open a laminate production
The main difficulty faced by entrepreneurs who decide to open such a serious business is the lack of high-quality raw materials that have to be purchased abroad. You can, of course, find domestic suppliers, but their raw materials will only be suitable for economy class laminate, and finding these suppliers is also a problem: there are not so many of them.
The next problem in organizing a business for the production of laminate flooring is the lack of norms and standards for the production of such materials in Russian legislation. Meanwhile, this issue is very acute, because the production technology involves the use of formaldehydes, which are part of chipboard boards. For this reason, businessmen have to focus on existing standards developed in other states.
Documents required to open a laminate production
In order for the business to begin to fully function, you need to take care of a package of permits in advance, the cost of which can reach up to several thousand dollars. In addition, it can take tens of months to obtain all permits and approvals. Here is a list of organizations you will need to apply to for permits:
- the mayor's office, its land allotment commission, its construction department;
- fire service, sanitary and epidemiological supervision;
- utilities (thermal, gas, water supply, electricians, signalmen).
After acceptance of the workshop into operation, you may also need permission from the labor protection services and the environmental department.
In order not to spend a lot of money and time on paperwork, you can immediately find a place for a workshop in an already finished woodworking workshop and place production in it.
Premises, equipment, raw materials for the production of laminate flooring
You should know that to launch a fully functioning plant, you will need a considerable area - about 2 - 2.5 thousand square meters. Moreover, this room should be dry, well ventilated and heated, because the laminate is a capricious material that does not like moisture. This must be taken into account in order to minimize the number of rejected products.
The equipment you need for production is a processing line, which consists of a double-sided profile machine, automatic cleaning, packing machine, automatic feeding / loading and automatic stacking. In addition, you will probably need a forklift to move the product.

The main suppliers of technological lines for the production of laminate flooring are the following companies: Barberan (Spain), Bürkle (Germany), LEDINEK (Russia, Moscow) and others. The list of equipment suppliers is small. There are about 10-15 enterprises in total.
With suppliers of raw materials, things are a little worse. There are only four companies worthy of attention: Elesgo and Homanit (in Germany), Korostensky MDF Plant (Ukraine) and MDF Woodworking Complex (Russia, Tyumen Region).
Personnel required for the production of laminate
The issue of personnel is quite complicated, since it is rather difficult to find qualified personnel today. It is likely that you will have to select the most suitable candidates in order to further train them, because some of them will work with complex equipment.
First of all, you need to hire employees in your company who will service and control the entire process of equipment operation. It is difficult to give specific advice on the number of personnel - it is better to find out from the manufacturer of this equipment how many people are intended to work with the line.
In addition, it is important not to forget to hire an electrician for the repair and maintenance of particularly complex equipment.
Do not forget to organize a warehouse for finished products and take a person responsible for organizing its work. Such an employee can take on the responsibility of receiving, posting goods, issuing products to the buyer and maintaining records. In addition, he could combine these duties with those of a forklift driver.
Another important person on the staff of any manufacturing company is the purveyor.
Do not forget about account managers, as well as accountants. Instead of organizing an accounting department, you can contact any company that provides outsourcing services and conclude an agreement with them for accounting services. In some cases, this turns out to be cheaper than maintaining a staff of accountants.
Again, advice on headcount is difficult to give. You need to evaluate the performance of your enterprise in order to draw some specific conclusions. To begin with, you can hire a minimum of personnel, and then, focusing on the situation, get the missing number.

How to attract customers and increase sales
The easiest way to increase the sales of your own products is to develop your own dealer network. It is recommended to do this even during the organization of the production process, since due to the high competition in this flooring segment, it can take a long time to find distribution channels.
Main distribution channels there may be various hypermarkets that rent their retail space to manufacturers and wholesalers with their own building materials stores. This method of marketing products has its pros and cons.
There is a big risk that your quality product may be lost in a huge variety of competitors' products, but on the other hand, this may be the only opportunity to sell products, especially when the company is young. Here it is important to communicate as closely as possible with wholesalers, who, as a rule, prefer inexpensive goods.

Another method, but it is less effective than the previous one, is mailings, personal meetings of sales managers, “hot” calls, and so on.
Another way to express yourself and your products is to participate in various exhibitions, which not only allow you to acquaint consumers with your products, but also allow you to conclude profitable contracts for the supply of your goods.
Another way is to install various advertising stands and pavement signs in crowded places.
There are, of course, other ways. For example, you can integrate your business into social networks by creating a group and gaining a large number of subscribers - your potential audience. And with the help of various posts to report on your news and thus form a positive opinion about you. This method can be both very effective and failure. Most importantly, it requires a competent approach and the work of a highly qualified specialist.

In order for your laminate flooring business to be profitable, it is not enough just to start it in production and recruit staff. Here an important role is played by market analysis and identification of the needs of your potential consumers, as well as a competent pricing policy.
But the most important thing is clearly and well-thought-out marketing moves and a good business plan, and the rest will follow.
designed to protect against external influences.
This is a special paper that imitates the structure and color of various tree species or ceramic tiles.
Laminate base, high density fibreboard.
designed to protect the HDF board from deformation and protect the laminate from moisture.
With the help of these locks, the laminate panels are tightly fastened together without the use of glue.
From HDF board with impregnation of the upper layers, this is a process consisting of the following steps:
plate lining;
cutting and milling panels;
package.
Impregnation is the impregnation of a material with special compounds. The upper layers of the laminate are impregnated with resins with various additives, which form a durable layer when cured. The strength and wear resistance of the top layer of the laminate, and hence its class, depend on the formulation of the impregnation compositions. Basically, laminate manufacturers do not impregnate the top layers, but buy them ready-made.
manufactures direct compression laminate DPL. With DPL technology, all layers of the laminate are simultaneously pressed at high temperature. This laminate production technology does not use glue, as layers that have undergone an impregnation process are used, which, when hot pressed (up to 200 ° C), melt and glue the surfaces. After curing, the resin and overlay become a monolithic surface layer of the laminate.
To obtain a laminated board, it is necessary to cover the HDF board with paper-resin films and an overlay.
The last important stage of production is the manufacture of a laminate of the required size. With the help of sawing equipment for laminate, laminate sheets are cut to the required dimensions. Each laminate manufacturer has their own laminate sizes. After cutting into plates, with the help of milling equipment, a tenon and a groove are cut out of the edges of the laminate. Modern HDF boards allow you to cut a tongue and groove of a certain profile, which are called laminate locks. With the help of these locks, the laminate panels are tightly fastened together without the use of glue. The quality, strength and tightness of the connection of laminate panels depends on the quality of the laminate lock and the strength of the HDF sheet.
There is a packaging in a thermoshrinkable polyethylene (PE) film of the finished laminate.

Comprises:
1. ZYX1400 laminating machine; ZYX1600.
2. Laminate sawing machines DP-2700.
3. Line for milling a click lock on FHZ525+FHH625 laminate.
4. TS-200 laminate packing machine.
The productivity of the line per shift (8 hours) is: 700 m2. Required area of the workshop (without a warehouse for finished products): 450 m2.
Automatic consists of the following main units:
1. .
2. Fan cooling line.
3. Laminate sawing line.
4. Laminate lock milling line.
5. Packing line for laminate flooring.
Line capacity per shift (8 hours) is: 1000 m2. Required area of the workshop (without a warehouse for finished products): 900 m2.
It is used in the production of laminate. manufactured for different sizes of HDF boards: 2800×2070 mm, 2440×1220 mm, 2440×2070 mm, 2620×2070 mm. High pressure presses "ZYX" have different productivity and pressing force, they are supplied with infeed and outfeed tables.
| Total pressure (t) | 1400 | 1600 |
| Specific pressure (kg/cm2) | 27,4 | 27,4 |
| Cylinder arrangement |
upper | upper |
| Hydraulic cylinder diameter (mm) |
340 | 380 |
| Number of hydraulic cylinders (pcs) |
6 | 6 |
| Productivity (pcs/day) | 1200 |
1200 |
| Plate size (mm) |
2440x1220 |
2620x2070 |
| Maximum plate opening (mm) | 200 |
200 |
| Boiler power (KW) | 31 | 31 |
| Overall dimensions, mm) | 3300x2000x3500 | 3700x2200x3500 |
| Machine weight (kg) | 17000 | 20000 |
Designed for transverse sawing of laminate to the required dimensions. Each manufacturer has its own dimensions of the laminate.

| Maximum slab width (mm) |
2700 |
| Maximum cutting height (mm) | 30 |
| Saw diameter (mm) |
180-250 |
| Landing diameter of saws (mm) |
75 |
| Saw speed (rpm) |
2500 |
| Total Power (KW) | 23,7 |
| Feeding speed (m/min) |
3-15 |
| Overall dimensions, mm) | 2000x3300x1350 |
| Machine weight (kg) | 3450 |
Designed for longitudinal sawing of the laminate to the required dimensions for subsequent milling of the laminate.

| Maximum slab width (mm) | 1250 |
| Cutting Height (mm) | 6-20 |
| Saw diameter (mm) | 300 |
| Landing diameter of saws (mm) | 80 |
| Saw speed (rpm) | 2900 |
| Feeding power (KW) | 1,1 |
| Main engine power (KW) | 15 |
| Feeding speed (m/min) | 10-40 |
| Overall dimensions, mm) | 1350x1200x1350 |
| Machine weight (kg) | 600 |
The automatic high-speed line is intended for production of the lock (Click) on a laminate. It is equipped with additional cutting spindles, which eliminates chips along the entire perimeter of the workpiece and guarantees the high quality of the finished product. The working surface of the table is equipped with hard-alloy plates, which ensures the durability of the equipment and reduces wear on the table surface. The receiving table is equipped with an automatic workpiece feeder to increase the feed rate up to 80 m/min.

 |
High torque German SEW electric motor with built-in industrial PID feed controller, achieving high feed speed of 80 m/min. |
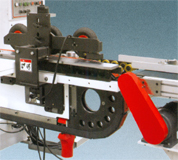 |
V-HOLD designed precision linear guides with carbide inserts for high speed feeds (increase wear resistance and reduce friction on the table). |
 |
Control system - SIEMENS with a multifunctional and intuitive interface, ease of management and configuration. |
 |
French air preparation system Legris. |
 |
supply of diamond tools. |
 |
Input material size control for safe operation. |
 |
High pressure air blower system that removes dust and chips from the rails and table. |
 |
Thickness control of the workpiece on the tenon cutter. |
 |
Table cover hardness HV-700-1000, hardness level YG8. |
 |
Patented vertical spindles for precision milling of parts. |
 |
Dustproof inverters from SIEMENS. |
 |
The combined feed system evenly distributes pressure over the entire area of the workpiece being machined. |
| Specifications | |
| Feeding speed (m/min) | 20-80 |
| 0,75 | |
| Dimensions (mm) | 3100x600x1400 |
| Maximum processing width (mm) | 250 |
| Minimum processing width (mm) | 95 |
| Feeding speed (m/min) | 20-80 |
| Feed drive power (KW) | 9 |
| 6000-8000 | |
| 6x8KW | |
| 4x6.5 kW | |
| 1,5 | |
| Spindle diameter (mm) | 40 |
| 280 | |
| 120 | |
| Total Power (KW) | 83 |
| Feeding speed (m/min) | 20-80 |
| Total Power (KW) | 2 |
| Dimensions (mm) | 2880x600x1400 |
| Maximum workpiece length (mm) | 2500 |
| Minimum workpiece length (mm) | 400 |
| Feeding speed (m/min) | 10-60 |
| Feed drive power (KW) | 5,5 |
| Spindle speed (rpm) | 6000-8000 |
| Power of vertical spindles | 6x6.5 kW |
| Finishing spindle power "Click" | 4x6.5 kW |
| Width adjustment motor power (KW) | 1,5 |
| Spindle diameter (mm) | 40 |
| Tool diameter on spindles (mm) | 220-250 |
| Suction nozzle diameter (mm) | 120 |
| Total Power (KW) | 92,6 |
It is intended for semi-automatic packaging in a thermoshrinkable PE film of a finished laminate.
In the finishing materials market, laminate is very popular and in special demand, making it a worthy competitor to various types of flooring, including parquet and solid floorboards. It is widely used in residential and office premises and is distinguished by ease of installation, operation and maintenance, luxurious appearance, resistance to mechanical stress and deformation, an ideal complement to any interior style, and a variety of colors.
Laminate production began in the late 70s of the last century in Sweden. The modern geography of its manufacture covers many countries of the world, including China, Russia, Ukraine.
Modern manufacturers offer finishing material with a variety of textures, patterns, photo printing with original images. The texture of the laminate is distinguished by an ideal picture of authenticity, imitating the surfaces of natural materials.
But the palm is still held by European companies that are distinguished by the development of new products, the improvement of equipment for the production of laminate and the development of innovative technologies. The quality of the flooring is controlled by the Association of European Laminate Flooring Manufacturers.
The composition of the laminated coating

The first manufacturers of laminate flooring offered a two-layer board.
Today it consists of four layers:
- The first layer of transparent durable resin film provides reliable protection against dirt, sun exposure, minor scratches, chemicals. Additionally, a layer of varnish can be applied to the surface to give shine. The class of the laminate is determined by the quality of the first layer.
- The second layer performs a decorative function and is a paper impregnated with resins. The perfect imitation of the texture of wood, stone, leather, granite, marble makes it difficult to distinguish between the laminate and the surface of natural materials.
- The third layer is the main one and for its creation a fibreboard is used, the density and quality of which determines the properties and characteristics of the floor covering. Its production is based on the method of pressing wood material with glue. This layer in the production of laminate is the bearing part of the coating.
- The fourth layer is designed to protect the floor finishing material from deformation, exposure to moisture, fumes, mold, fungus and provide increased rigidity and stability. It is a cardboard impregnated with resins, paraffin or high density melamine film.
The main stages of the production of flooring
The production of a laminated coating involves the implementation of several stages.

The main ones include:
- production of high-density fibreboard;
- processing of flooring sheets with special compounds;
- cladding, laminate lamination;
- sawing, milling and packaging of finished products.
Production of fibreboard
Fibreboards serve as load-bearing parts of the floor covering. Their production is based on carrying out many operations.
These include:
- grinding wood without bark to obtain small chips, which serve as a raw material for the production of laminate;
- washing chips to remove dirt, sand, impurities;
- two-stage steaming of chips with steam at a temperature of 100°C and 175°C to obtain material of the same moisture content and plasticity;
- grinding in a refiner to the desired fraction of raw materials;
- the addition of resins, paraffin, binders, increasing the density of the plate and reducing moisture absorption;
- wood chips drying in accordance with the laminate production technology;
- primary pressing of chips to form the surface of the plate under a pressure of 300 MPa and a temperature of 300°C;
- heating pressing of the material at a temperature of 190°C under pressure from 40 MPa to 120 MPa;
- leveling the slab until a perfectly flat surface is obtained.

The production of fiberboards is the most important stage in the technological process in the production of laminate.
Impregnation or impregnation of boards with special compounds
The plates prepared for further processing, in accordance with the technology of laminate production, undergo impregnation based on the impregnation of the material with special compounds.
For the top layer, resins with additives are used to provide a durable layer after hardening and determine the degree of wear resistance, as well as the life of the floor covering. Sometimes corundum particles are added to the composition, designed to improve the quality characteristics of the finishing material.
Facing stage
Facing, provided by the production technology of laminated panels, is carried out in two ways. The first of these is called caching. It is based on the application of an adhesive with a hardener to the upper layers of the laminate and their subsequent pressing. The process is carried out at high temperatures and may involve the surfaces of the coating that have passed and have not passed the impregnation stage.
The second cladding method involves pressing all laminate layers without the use of glue. It is designed for boards impregnated with special compounds.
The final stage
At the final stage of laminate production, the sawing, milling of the flooring and cutting out the fasteners on the edge side of the board are performed. Sometimes the technology for the production of laminate flooring provides for the application of wax or paraffin on the edge sides of the board.

After passing through all stages of production, the material is packed in a polyethylene film manually or mechanically.






